publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2024
- ACS Omega
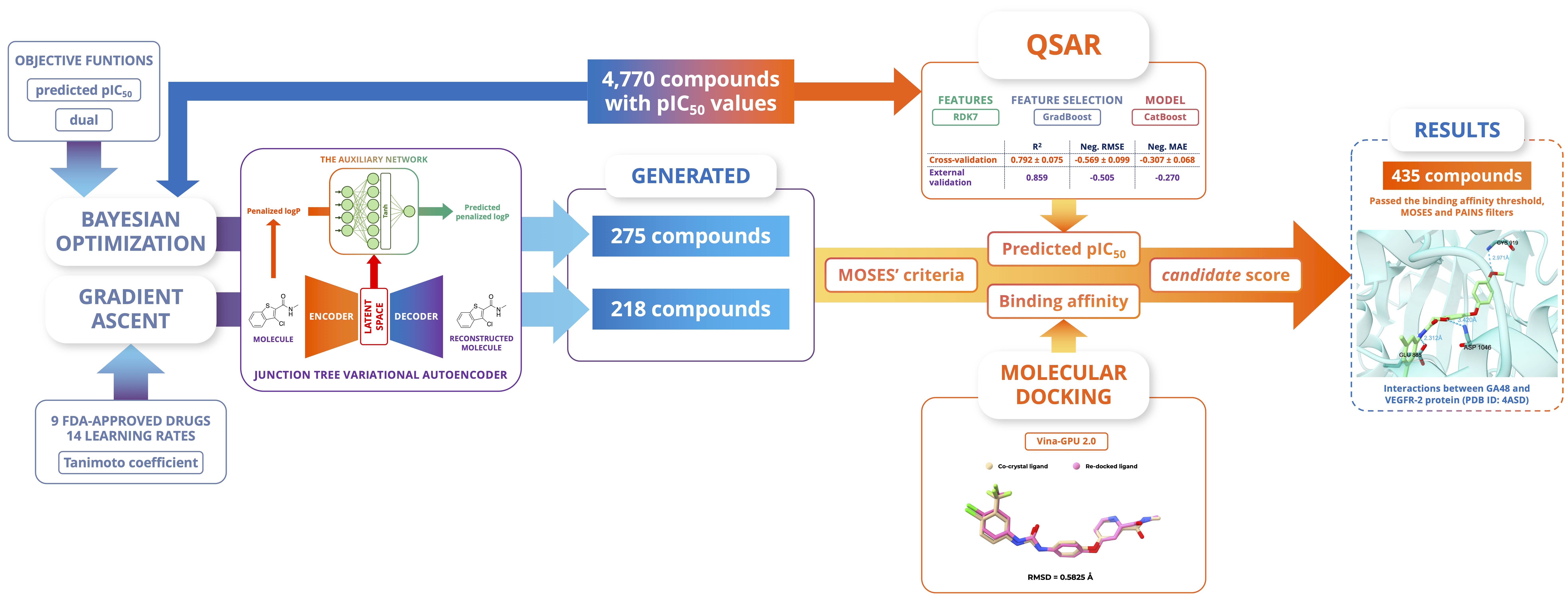 Discovery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 Inhibitors Employing Junction Tree Variational Autoencoder with Bayesian Optimization and Gradient AscentGia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Van-Thinh To, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, The-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongACS Omega, 2024
Discovery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 Inhibitors Employing Junction Tree Variational Autoencoder with Bayesian Optimization and Gradient AscentGia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Van-Thinh To, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, The-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongACS Omega, 2024In the development of anticancer medications, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), which belongs to the protein tyrosine kinase family, emerges as one of the most significant targets of interest. The ongoing Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of novel therapeutic medicines toward VEGFR-2 emphasizes the urgent need to discover sophisticated molecular structures that are capable of reliably limiting VEGFR-2 activity. Recognizing the huge potential of deep-learning-based molecular model advancements, we focused our study on exploring the chemical space to find small molecules potentially inhibiting VEGFR-2. To achieve this goal, we utilized the junction tree variational autoencoder in combination with two optimization approaches on the latent space: the local Bayesian optimization on the initial data set and the gradient ascent on nine FDA-approved drugs targeting VEGFR-2. The optimization results yielded a set of 493 uncharted small molecules. Quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) models and molecular docking were used to assess the generated molecules for their inhibitory potential using their predicted pIC50 and binding affinity. The QSAR model constructed on RDK7 fingerprints using the CatBoost algorithm achieved remarkable coefficients of determination (R2) of 0.792 ± 0.075 and 0.859 with respect to internal and external validation. Molecular docking was implemented using the 4ASD complex with optimistic retrospective control results (the ROC-AUC value was 0.710 and the binding activity threshold was −7.90 kcal/mol). Newly generated molecules possessing acceptable results corresponding to both assessments were shortlisted and checked for interactions with the protein at the binding site on important residues, including Cys919, Asp1046, and Glu885.
@article{vegfr2, title = {Discovery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 Inhibitors Employing Junction Tree Variational Autoencoder with Bayesian Optimization and Gradient Ascent}, author = {Truong, Gia-Bao and Pham, Thanh-An and To, Van-Thinh and Lai Le, Hoang-Son and Van Nguyen, Phuoc-Chung and Trinh, The-Chuong and Phan, Tieu-Long and Truong, Tuyen Ngoc}, keywords = {Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, junction tree variational autoencoder, bayesian optimization, gradient ascent}, doi = {10.1021/acsomega.4c07689}, url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.4c07689}, journal = {ACS Omega}, year = {2024}, } - ChemRxiv
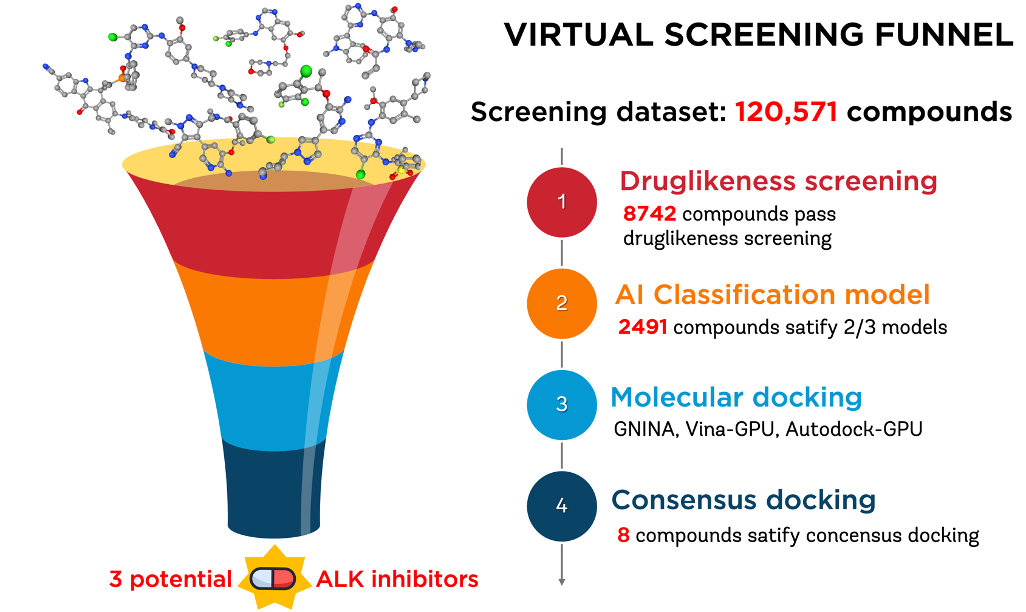 SYNERGY OF ADVANCED MACHINE LEARNING AND DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS WITH CONSENSUS MOLECULAR DOCKING FOR ENHANCED POTENCY PREDICTION OF ALK INHIBITORSThe-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, Van-Thinh To, Thanh-An Pham, Gia-Bao Truong, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Xuan-Truc Tran, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongChemRxiv, 2024
SYNERGY OF ADVANCED MACHINE LEARNING AND DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS WITH CONSENSUS MOLECULAR DOCKING FOR ENHANCED POTENCY PREDICTION OF ALK INHIBITORSThe-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, Van-Thinh To, Thanh-An Pham, Gia-Bao Truong, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Xuan-Truc Tran, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongChemRxiv, 2024This study addresses the urgent need for novel Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) treatment, focusing on the ALK-positive mutation variant (5% of the cases). As only five Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved ALK inhibitors are on the market, the demand for effective drugs persists. Leveraging the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) including machine learning (ML), and deep learning, our research aimed to expedite the screening of novel ALK inhibitors. Notably, the machine learning-based XGBoost algorithm exhibited compelling results with an external validation (EV)-f1 score of 0.921, and an EV-Average Precision (AP) of 0.961, alongside a cross-validation (CV)-f1 score of 0.888±0.039 and a CV-AP of 0.939±0.032. Besides, the deep learning-based Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model demonstrated excellent performance with an EV-f1 score of 0.930 and an EV-AP of 0.955, complemented by a CV-f1 score of 0.891±0.037 and a CV-AP of 0.934±0.040. The present study undertook a comparative analysis between the traditional ML models, the ANN model, and the Graph Neural Network (GNN) model, which is a product of our recent research endeavors. The findings reveal that, despite the advancements in neural network models, traditional machine learning models exhibited superior performance over the GNN model. During this research, these models were employed in conjunction with a consensus molecular docking model to screen a total of 120,571 compounds virtually, leading to the identification of three promising ALK inhibitors: CHEMBL1689515, CHEMBL2380351, and CHEMBL102714. The study recommends further molecular dynamic simulations, in vitro tests, target-specific experimental data acquisition for active learning, and application of advanced AI models like geometric interaction GNN and generative AI for molecular optimization.
@article{alk, title = {SYNERGY OF ADVANCED MACHINE LEARNING AND DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS WITH CONSENSUS MOLECULAR DOCKING FOR ENHANCED POTENCY PREDICTION OF ALK INHIBITORS}, author = {Trinh, The-Chuong and Phan, Tieu-Long and To, Van-Thinh and Pham, Thanh-An and Truong, Gia-Bao and Lai Le, Hoang-Son and Tran, Xuan-Truc and Truong, Tuyen Ngoc}, keywords = {ALK, computer-aided drug design, artificial intelligence, machine learning, benchmarking, consensus molecular docking}, doi = {10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-xpfm1}, year = {2024}, journal = {ChemRxiv}, }
2023
- KSE 2023
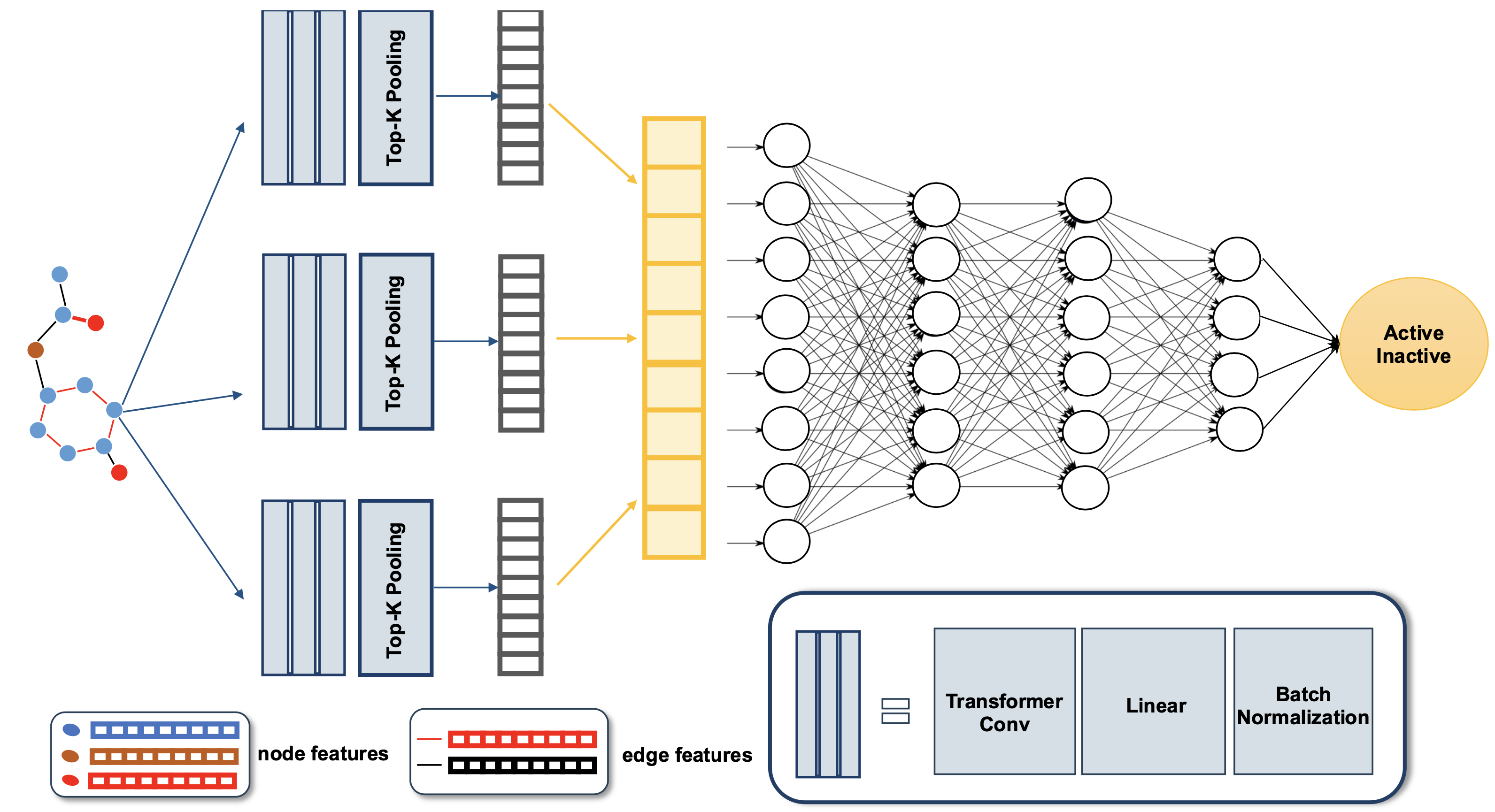 A Graph Neural Network Model Enables Accurate Prediction of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors Compared to Other Machine Learning ModelsThe-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, Van-Thinh To, Gia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongIn 2023 15th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), 2023
A Graph Neural Network Model Enables Accurate Prediction of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors Compared to Other Machine Learning ModelsThe-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, Van-Thinh To, Gia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongIn 2023 15th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), 2023Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), a tyrosine kinase receptor, is identified as a crucial target in the progression of anticancer therapeutics for non-small cell lung cancer. This study has executed a Graph Neural Network (GNN) model and compared it with three machine learning (ML) models based on fingerprints for rapid anticancer bioactivity prediction. ALK inhibitors with IC50 values were extracted from the REAXYS database. Following preprocessing, these inhibitors constituted a dataset of 1664 molecules. Subsequently, GNN and ML models were constructed on a training set. The generalizability of these models was assessed by internal and external validation procedures. The graph neural network model yielded promising results, with an average precision of 0.879±0.041 and an F1 score of 0.804±0.049 in cross-validation. In external validation, the model achieved an average precision of 0.938 and an F1 score of 0.863, surpassing the results of the ML models. Therefore, we can infer that the predictive model developed using the GNN is apt for the problem at hand and can be utilized to predict the biological activity of novel ALK inhibitors.
@inproceedings{kse, author = {Trinh, The-Chuong and Phan, Tieu-Long and To, Van-Thinh and Truong, Gia-Bao and Pham, Thanh-An and Lai Le, Hoang-Son and Van Nguyen, Phuoc-Chung and Ngoc Truong, Tuyen}, booktitle = {2023 15th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE)}, title = {A Graph Neural Network Model Enables Accurate Prediction of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors Compared to Other Machine Learning Models}, year = {2023}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1--6}, keywords = {Training,Knowledge engineering,Inhibitors,Biological system modeling,Lung cancer,Machine learning,Predictive models,Anaplastic lymphoma kinase,NSCLC,Graph neural network,Machine learning,Benchmarking}, doi = {10.1109/KSE59128.2023.10299477}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10299477}, } - AFPS 2023
 Innovative Exploration of VEGFR-2 Inhibitors in chemical space with Gradient Ascent and Junction Tree Variational AutoencoderGia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Van-Thinh To, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, The-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongAsian Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, Ha Noi, Vietnam (Poster presenter) , 2023
Innovative Exploration of VEGFR-2 Inhibitors in chemical space with Gradient Ascent and Junction Tree Variational AutoencoderGia-Bao Truong, Thanh-An Pham, Van-Thinh To, Hoang-Son Lai Le, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, The-Chuong Trinh, Tieu-Long Phan, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongAsian Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, Ha Noi, Vietnam (Poster presenter) , 2023@misc{afps2023_vegfr2, author = {Truong, Gia-Bao and Pham, Thanh-An and To, Van-Thinh and Lai Le, Hoang-Son and Van Nguyen, Phuoc-Chung and Trinh, The-Chuong and Phan, Tieu-Long and Truong, Tuyen Ngoc}, title = {Innovative Exploration of VEGFR-2 Inhibitors in chemical space with Gradient Ascent and Junction Tree Variational Autoencoder}, year = {2023}, } - AFPS 2023
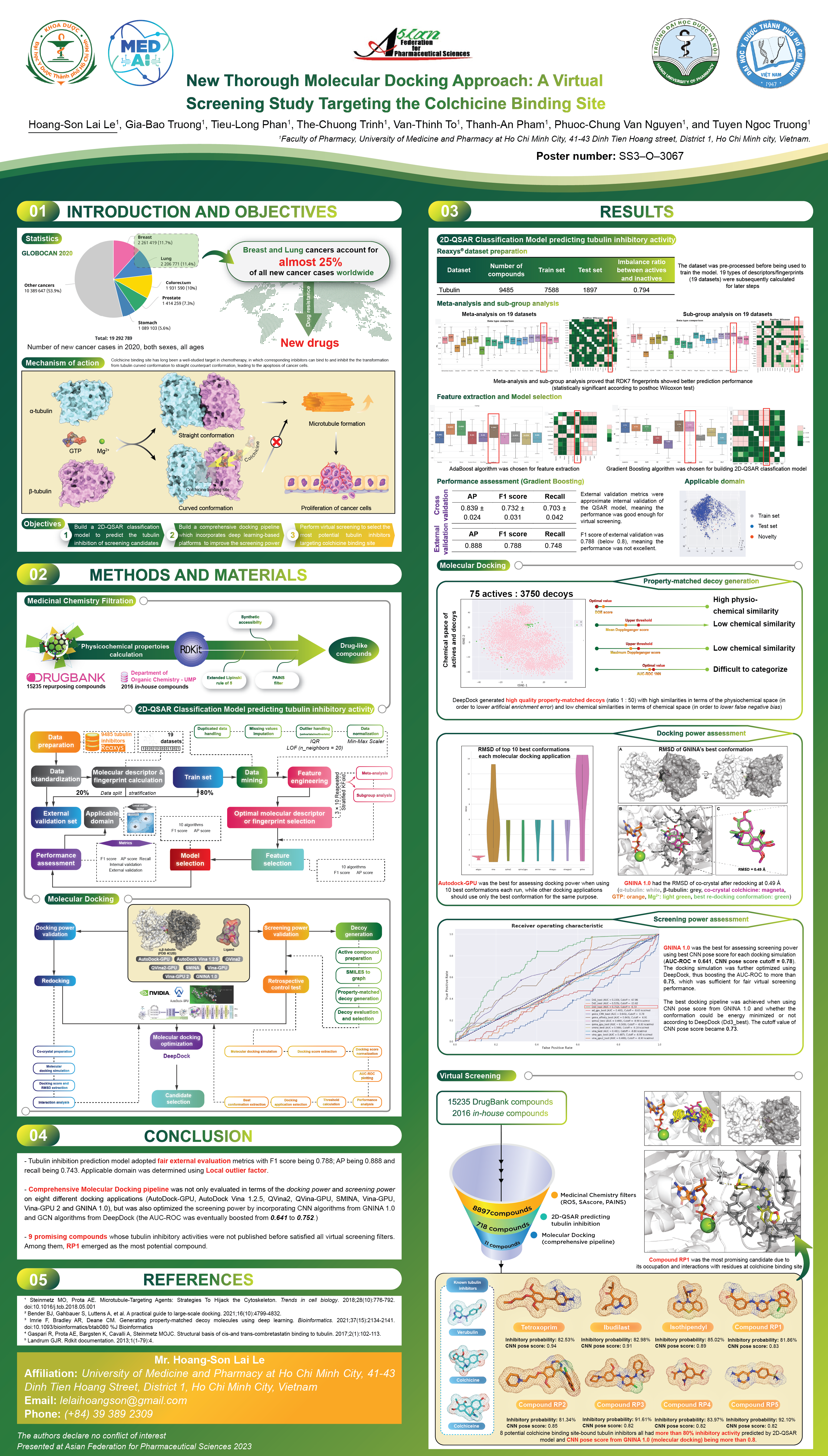 New Thorough Molecular Docking Approach: A Virtual Screening Study Targeting the Colchicine Binding SiteHoang-Son Lai Le, Tieu-Long Phan, Gia-Bao Truong, The-Chuong Trinh, Van-Thinh To, Thanh-An Pham, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongAsian Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, Ha Noi, Vietnam (Best poster) , 2023
New Thorough Molecular Docking Approach: A Virtual Screening Study Targeting the Colchicine Binding SiteHoang-Son Lai Le, Tieu-Long Phan, Gia-Bao Truong, The-Chuong Trinh, Van-Thinh To, Thanh-An Pham, Phuoc-Chung Van Nguyen, and Tuyen Ngoc TruongAsian Federation for Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, Ha Noi, Vietnam (Best poster) , 2023@misc{afps2023_docking, author = {Lai Le, Hoang-Son and Phan, Tieu-Long and Truong, Gia-Bao and Trinh, The-Chuong and To, Van-Thinh and Pham, Thanh-An and Van Nguyen, Phuoc-Chung and Truong, Tuyen Ngoc}, title = {New Thorough Molecular Docking Approach: A Virtual Screening Study Targeting the Colchicine Binding Site}, year = {2023}, }
